27-1-负载均衡策略
以下为你详细介绍几种常见的负载均衡(LB)调度算法,并通过 Mermaid 图表进行直观展示。
1. 轮询算法(Round Robin)
原理
轮询算法按顺序依次将客户端的请求分配到后端服务器列表中的每一台服务器,当所有服务器都分配过一次后,再从头开始循环。
Mermaid 代码
graph LR
classDef client fill:#E5F6FF,stroke:#73A6FF,stroke-width:2px
classDef lb fill:#FFF6CC,stroke:#FFBC52,stroke-width:2px
classDef server fill:#FFEBEB,stroke:#E68994,stroke-width:2px
A([客户端请求]):::client --> B(负载均衡器):::lb
B --> C(服务器 1):::server
B --> D(服务器 2):::server
B --> E(服务器 3):::server
C --> F([响应结果]):::client
D --> F
E --> F
F --> B
B --> A
linkStyle 0,1,2,3,4,5 stroke:#007BFF,stroke-width:2px
解释
客户端发出请求到负载均衡器,负载均衡器按顺序把请求依次分配给服务器 1、服务器 2、服务器 3,之后再从服务器 1 开始新一轮分配。
2. 加权轮询算法(Weighted Round Robin)
原理
为每台后端服务器分配一个权重值,权重越高,表明该服务器的处理能力越强。负载均衡器根据服务器的权重比例来分配请求。
Mermaid 代码
graph LR
classDef client fill:#E5F6FF,stroke:#73A6FF,stroke-width:2px
classDef lb fill:#FFF6CC,stroke:#FFBC52,stroke-width:2px
classDef server fill:#FFEBEB,stroke:#E68994,stroke-width:2px
A([客户端请求]):::client --> B(负载均衡器):::lb
B -->|权重 3| C(服务器 1):::server
B -->|权重 2| D(服务器 2):::server
B -->|权重 1| E(服务器 3):::server
C --> F([响应结果]):::client
D --> F
E --> F
F --> B
B --> A
linkStyle 0,1,2,3,4,5 stroke:#007BFF,stroke-width:2px
解释
假设服务器 1 权重为 3,服务器 2 权重为 2,服务器 3 权重为 1。负载均衡器分配请求时,会按服务器 1、服务器 1、服务器 1、服务器 2、服务器 2、服务器 3 的顺序进行。
3. IP 哈希算法(IP Hash)
原理
根据客户端的 IP 地址进行哈希计算,将计算结果与后端服务器列表进行映射,使得同一个客户端的请求始终被分配到同一台后端服务器上。
Mermaid 代码
graph LR
classDef client fill:#E5F6FF,stroke:#73A6FF,stroke-width:2px
classDef lb fill:#FFF6CC,stroke:#FFBC52,stroke-width:2px
classDef server fill:#FFEBEB,stroke:#E68994,stroke-width:2px
A([客户端 1 请求]):::client --> B(负载均衡器):::lb
C([客户端 2 请求]):::client --> B
B -->|哈希映射| D(服务器 1):::server
B -->|哈希映射| E(服务器 2):::server
D --> F([响应结果]):::client
E --> F
F --> B
B --> A
B --> C
linkStyle 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7 stroke:#007BFF,stroke-width:2px
解释
客户端 1 和客户端 2 发出请求到负载均衡器,负载均衡器通过对它们的 IP 地址进行哈希计算,将客户端 1 的请求一直分配给服务器 1,客户端 2 的请求一直分配给服务器 2。
4. 最少连接算法(Least Connections)
原理
负载均衡器实时监控每台后端服务器的连接数,将新的请求分配给当前连接数最少的服务器。
Mermaid 代码
graph LR
classDef client fill:#E5F6FF,stroke:#73A6FF,stroke-width:2px
classDef lb fill:#FFF6CC,stroke:#FFBC52,stroke-width:2px
classDef server fill:#FFEBEB,stroke:#E68994,stroke-width:2px
classDef decision fill:#D5F5E3,stroke:#58D68D,stroke-width:2px
A([客户端请求]):::client --> B(负载均衡器):::lb
B --> C{选择连接最少的服务器}:::decision
C -->|连接数 2| D(服务器 1):::server
C -->|连接数 5| E(服务器 2):::server
C -->|连接数 3| F(服务器 3):::server
D --> G([响应结果]):::client
E --> G
F --> G
G --> B
B --> A
linkStyle 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7 stroke:#007BFF,stroke-width:2px
解释
客户端请求到达负载均衡器后,负载均衡器查看各服务器的连接数,由于服务器 1 连接数最少,所以将请求分配给服务器 1。
一、lb调度算法
调度算法一般分几类:
- 第一类是静态调度算法:负载均衡器根据自身设定的规则进行分配,不需要考虑后端节点的健康情况。例如轮询、加权轮询、哈希类型调度算法。
- 第二类是动态调度算法,负载均衡器会判断后端节点的当前状态,来决定是否分发请求。例如链接数最少的优先分发,响应时间短的优先分发,如least_conn、fail等都是动态调度。
rr轮询(round-robin)
按照请求顺序逐一分配给不同的后端节点服务器,如果后端节点宕机,宕机的服务器会被自动从地址池中剔除,新的请求会发给正常的服务器。
Weight(权重轮询)
给后端节点服务器增加权重,数值越大,优先获得客户端请求,可以以服务器配置来决定比例大小,从而解决新旧服务器的性能不均衡问题等。
upstream backend {
server 192.168.178.122 weight=1;
server 192.168.178.121 weight=2;
}
ip_hash
每个请求按客户端IP的hash结果分配,当新的请求到达,将其客户端IP通过哈希算法得到一个唯一值,在随后的客户端请求中,如果客户端的IP哈希值相等,该请求就会固定发给一台服务器。
该调度算法可以解决动态网页中的session共享问题。
注意了使用ip_hash不得再使用weight、backup两个参数,造成冲突了,即使写了也不生效。
upstream chaoge_backend {
ip_hash;
server 192.168.178.121;
server 192.168.178.122;
}
url_hash
根据访问url的hash结果分配,同一个url固定发给一个后端节点。
least_conn
该算法根据后端节点的链接数决定分配请求,哪个机器链接数少,就发给谁。
实践
weight权重实践
按比例分配
[root@lb-5 /etc/nginx/conf.d]#cat proxy.conf
upstream web-pools {
server 172.16.1.7:8080 weight=2;
server 172.16.1.8:8080 weight=8;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name wordpress.yuchaoit.cn;
location / {
proxy_pass http://web-pools;
include /etc/nginx/proxy_params.conf;
}
}
[root@lb-5 /etc/nginx/conf.d]#systemctl restart nginx
- 此时是二、八开,也就是
1:4的比率

ip_hash实践
和ip_hash类似,该算法根据客户端请求的URL信息进行hash得到唯一值,让每个URL固定的发给同一个后端服务器,后端服务器为缓存服务器效果最佳。
Nginx本身是不支持url_hash的,需要单独安装hash模块
url_hash(web缓存节点)和ip_hash(会话保持)功能类似。
[root@lb-5 /etc/nginx/conf.d]#cat proxy.conf
upstream web-pools {
ip_hash;
server 172.16.1.7:8080 ;
server 172.16.1.8:8080 ;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name wordpress.yuchaoit.cn;
location / {
proxy_pass http://web-pools;
include /etc/nginx/proxy_params.conf;
}
}
[root@lb-5 /etc/nginx/conf.d]#systemctl restart nginx
使用10.0.0.xx网段的ip访问,发现被固定发给了web-8。

使用172.16.1.xx网段的ip访问,发现被固定发给了web-7。
体现ip_hash的作用。

url_hash实践
[root@lb-5 /etc/nginx/conf.d]#nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
[root@lb-5 /etc/nginx/conf.d]#cat proxy.conf
upstream web-pools {
hash $request_uri;
server 172.16.1.7:8080 ;
server 172.16.1.8:8080 ;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name wordpress.yuchaoit.cn;
location / {
proxy_pass http://web-pools;
include /etc/nginx/proxy_params.conf;
}
}
[root@lb-5 /etc/nginx/conf.d]#systemctl restart nginx

总结
目前了解参数具体用法与效果即可,具体是否添加该参数,要结合实际运维环境,否则可能会导致反向代理异常,因此初期先别用关于hash的参数,一般轮训,或者weight即可。
二、lb调度参数
参数作用
backup
被标记为backup参数的服务器,只有服务器池内的其他机器都无法访问了,才会使用该该机器。
max_failes
允许请求失败的次数,一般和fail_timeout结合用
fail_timeout
经过max_failes失败后服务暂停的时间。
down
标记这个机器停止使用了。
max_conns
限制最大接收的连接数。
参数实验
down参数
[root@lb-5 /etc/nginx/conf.d]#cat proxy.conf
upstream web-pools {
server 172.16.1.7:8080 down;
server 172.16.1.8:8080;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name wordpress.yuchaoit.cn;
location / {
proxy_pass http://web-pools;
include /etc/nginx/proxy_params.conf;
}
}
[root@lb-5 /etc/nginx/conf.d]#systemctl restart nginx
- 确保web-7,和web-8都正常运行后端服务。
- 检测日志

- 此时如果web-8挂了,会导致网站502。
然后可以调换down参数的位置,再试试
backup实验
[root@lb-5 /etc/nginx/conf.d]#cat proxy.conf
upstream web-pools {
server 172.16.1.7:8080 backup;
server 172.16.1.8:8080 ;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name wordpress.yuchaoit.cn;
location / {
proxy_pass http://web-pools;
include /etc/nginx/proxy_params.conf;
}
}
- web-7被标记为备份机器
- 请求只会发给web-8
- web-8宕机后,web-7会接替工作。

max_fails和fail_timeout参数
用于nginx探测后端节点是否异常的参数,默认是在10s内,允许某一个节点是宕机的,会把请求交给另外一个节点处理。
简单说就是,在10秒内,出现1次不可用,就判断这个节点是的故障的,且判定后的10秒内不会再发给这个节点,直到10s后的下一次探测。
[root@lb-5 /etc/nginx/conf.d]#cat proxy.conf
upstream web-pools {
server 172.16.1.7:8080 weight=1 fail_timeout=10s max_fails=1;
server 172.16.1.8:8080 weight=1 fail_timeout=10s max_fails=1;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name wordpress.yuchaoit.cn;
location / {
proxy_pass http://web-pools;
include /etc/nginx/proxy_params.conf;
}
}
[root@lb-5 /etc/nginx/conf.d]#systemctl restart nginx
这个参数不易测试,因为某一个节点挂掉,nginx也会把请求发给另外一个节点,因此了解即可。
故障实践
思考问题,如果web-8的php突然挂了,客户端访问情况会是如何?以及如何看待这个问题。
1. 测试 systemctl stop nginx
2. 测试 systemctl stop php-fpm
三、根据用户client_agent判断转发
需求
1. 如果用户是iphone跳转到iphone页面
2. 如果用户是Android跳转的android页面
3. 如果用户是PC端,跳转到PC页面
4. 如果用户是IE浏览器,提示他该升级电脑了。。。IE已经被世界淘汰了。
nginx配置文件
vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/huya.yuchaoit.conf
# 这里是简单用法,更精确的应该是配置如 m.huya.com这样的移动端虚拟主机
upstream android {
server 172.16.1.7:33333;
}
upstream iphone {
server 172.16.1.8:33333;
}
upstream pc {
server 172.16.1.7:22222;
server 172.16.1.8:22222;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name huya.yuchaoit.cn;
location / {
# 默认页面,交给pc
proxy_pass http://pc;
include proxy_params.conf;
# 判断是iphone用户,基于正则且不区分大小写
if ($http_user_agent ~* "iphone"){
proxy_pass http://iphone;
}
# 判断是安卓用户
if ($http_user_agent ~* "android"){
proxy_pass http://android;
}
# 如果是IE,禁止访问
if ($http_user_agent ~* "msie"){
return 403 "禁止访问!!IE被淘汰了都。。抓紧升级吧老哥\n";
}
}
}
重启lb-5
[root@lb-5 /etc/nginx/conf.d]#nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
[root@lb-5 /etc/nginx/conf.d]#
[root@lb-5 /etc/nginx/conf.d]#systemctl restart nginx
创建web机器组的PC页面
web-7
# 先创建 pc页面
cat > /etc/nginx/conf.d/pc.conf<<EOF
server {
listen 22222;
server_name _;
charset utf-8;
location / {
root /test-pc/;
index index.html;
}
}
EOF
# 创建pc页面
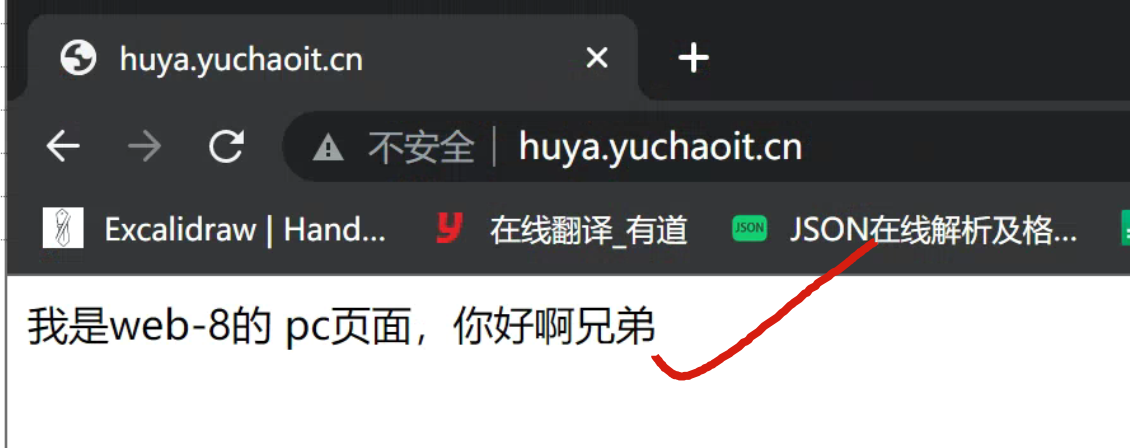
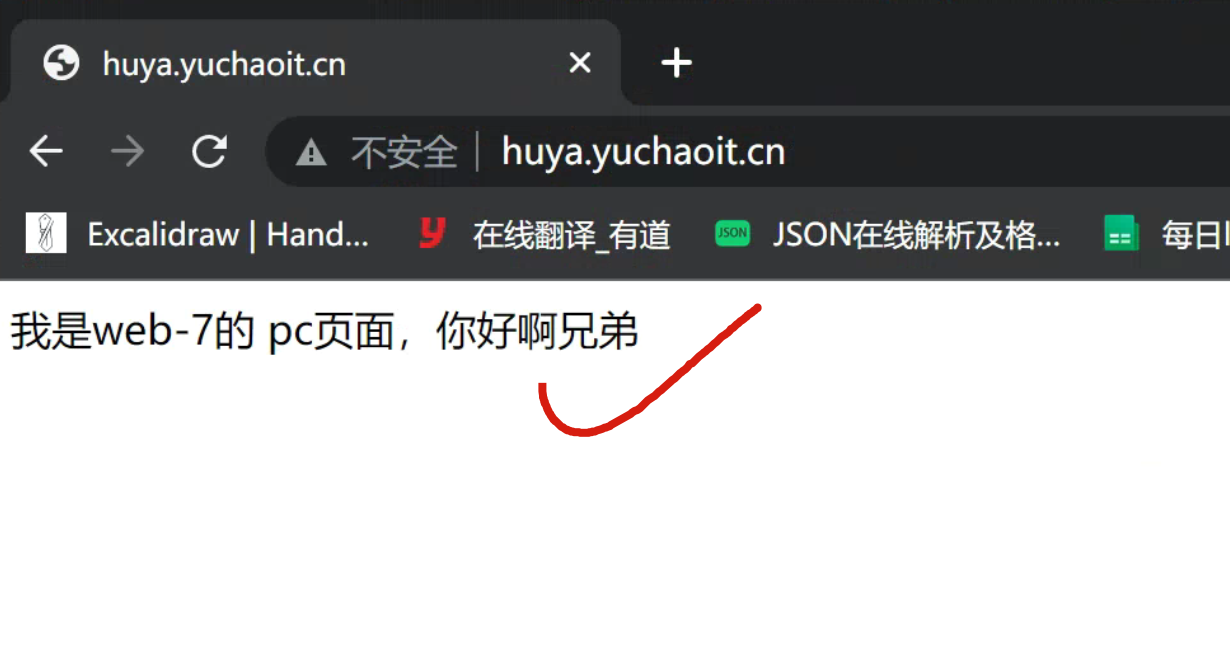
mkdir -p /test-pc/ ; echo '我是web-7的 pc页面,你好啊兄弟' > /test-pc/index.html
# 重启
systemctl restart nginx
web-8
# 先创建 pc页面
cat > /etc/nginx/conf.d/pc.conf<<EOF
server {
listen 22222;
server_name _;
charset utf-8;
location / {
root /test-pc/;
index index.html;
}
}
EOF
# 创建pc页面
mkdir -p /test-pc/ ; echo '我是web-8的 pc页面,你好啊兄弟' > /test-pc/index.html
# 重启
systemctl restart nginx
创建web机器组的移动端页面
我们这里是基于端口的虚拟主机,去模拟移动端页面,更精准的是设置域名,但是道理一样的。
web-7
cat > /etc/nginx/conf.d/m.conf<<EOF
server {
listen 33333;
server_name _;
charset utf-8;
location / {
root /test-m/;
index index.html;
}
}
EOF
mkdir -p /test-m/ ; echo '我是web-7的 移动端页面,你瞅啥?小老弟' > /test-m/index.html
systemctl restart nginx
web-8
cat > /etc/nginx/conf.d/m.conf<<EOF
server {
listen 33333;
server_name _;
charset utf-8;
location / {
root /test-m/;
index index.html;
}
}
EOF
mkdir -p /test-m/ ; echo '我是web-8的 移动端页面,你瞅啥?小老弟' > /test-m/index.html
systemctl restart nginx
访问lb机器
设置dns解析
10.0.0.5 www.yuchaoit.cn wecenter.yuchaoit.cn wordpress.yuchaoit.cn huya.yuchaoit.cn
最终图解正确结果
pc页面
移动端iphone
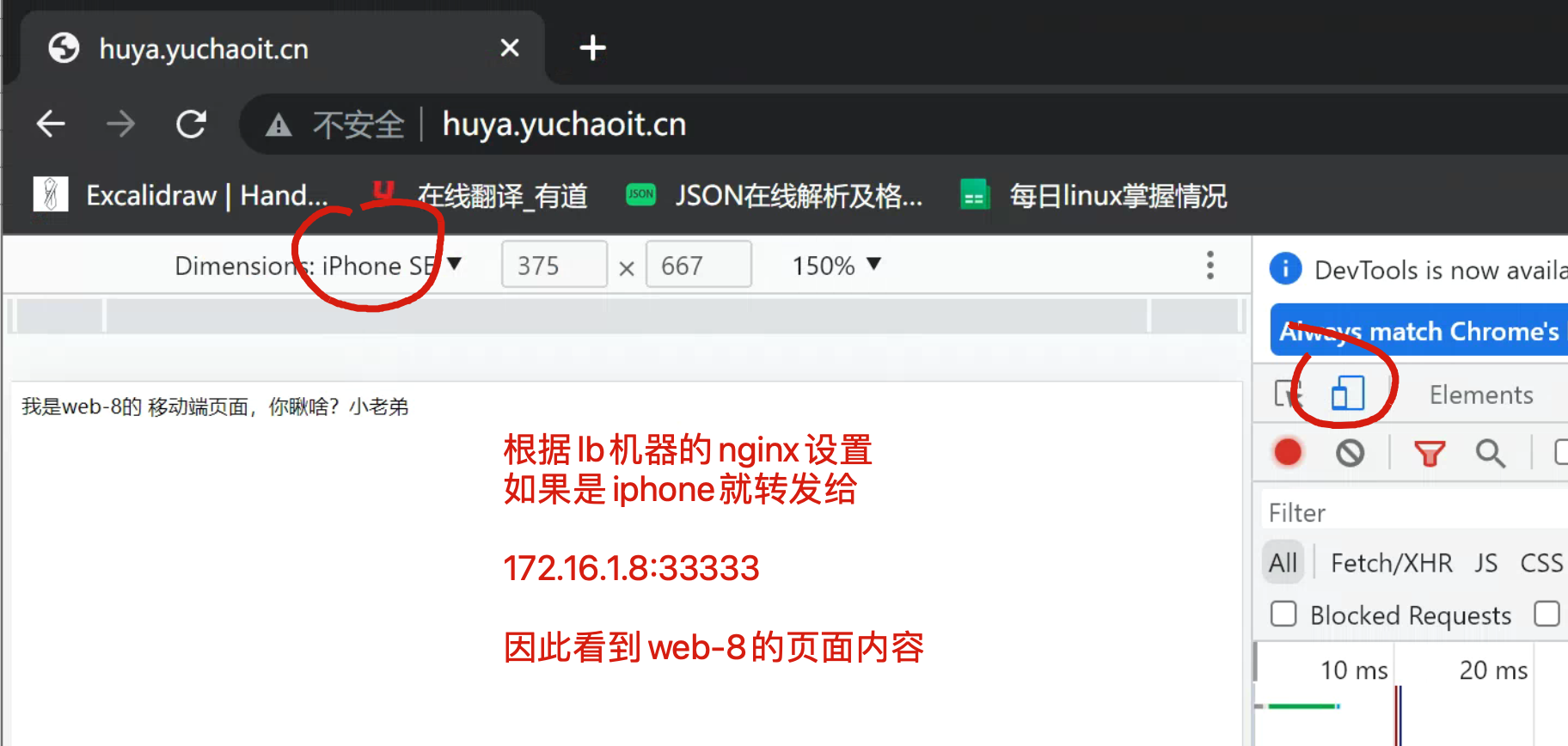
移动端安卓
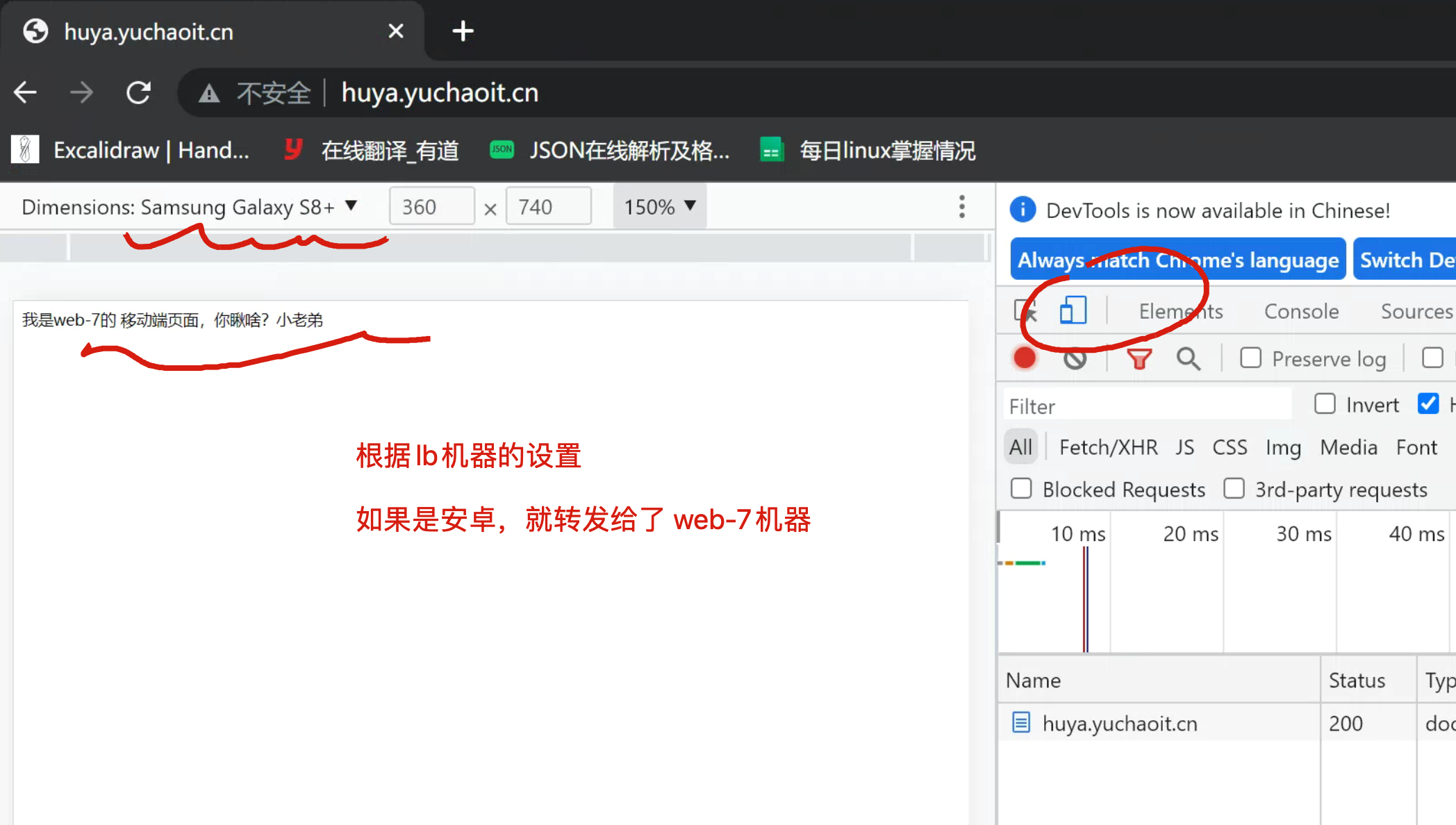
测试ie浏览器
[root@lb-5 /etc/nginx]#tail -1 /etc/hosts
10.0.0.5 huya.yuchaoit.cn
[root@lb-5 /etc/nginx]#curl -A 'msie' huya.yuchaoit.cn
禁止访问!!IE被淘汰了都。。抓紧升级吧老哥
[root@lb-5 /etc/nginx]#
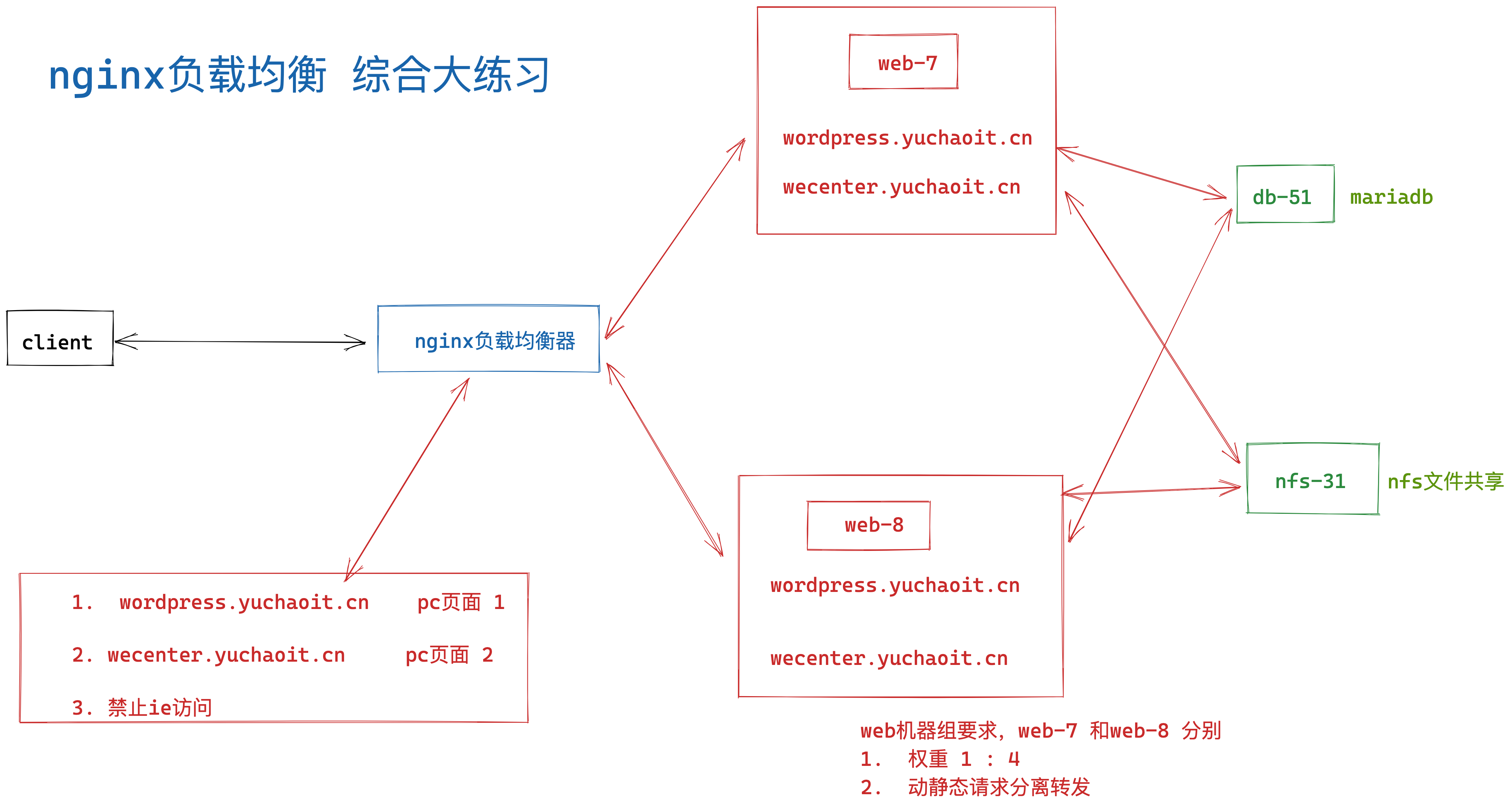
四、大作业
1.完成nginx负载均衡笔记
2.部署好wordpress、wecenter网站
- 你现在作为运维,要给公司上线如下两个网站,提供域名访问,且做好负载均衡。
使用机器
lb-5
web-7 wordpress.yuchaoit.cn wecenter.yuchaoit.cn
web-8 wordpress.yuchaoit.cn wecenter.yuchaoit.cn
并且实现即使随便关掉一个web机器,网站也不会宕机。
并且按照如下架构图部署